Selection sort:
In computer science, selection sort is an in-place comparison sorting algorithm. It has an O(n2) time complexity, which makes it inefficient on large lists, and generally performs worse than the similar insertion sort. Selection sort is noted for its simplicity and has performance advantages over more complicated algorithms in certain situations, particularly where auxiliary memory is limited.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void selectionSort(int *arr, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[i] > arr[j])
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
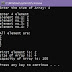
int arr[] = {23, 55, 1, 551, 6, 4, 432}; // example inputs
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// array before sorting
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) // for printing elements of array
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
selectionSort(arr, n); // selection sort function
// array after sorting
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) // for printing elements of array
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
23 55 1 551 6 4 432
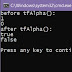
1 4 6 23 55 432 551


No comments:
Post a Comment